Scientific Modeling Workflows
Terarium supports scientific decision making by helping users organize, refine, and communicate the results of their modeling processes. Users can:
- Gather existing knowledge.
- Break down complex scientific operations into separate, easy-to-configure tasks.
- Create reproducible visual representations of how resources, processes, and results chain together.
Table of contents
Building transparent, reproducible workflows
The Terarium workspace is a visual canvas for building and capturing modeling processes. Workflows show how resources (models, datasets, and documents) move between different operators to produce results.
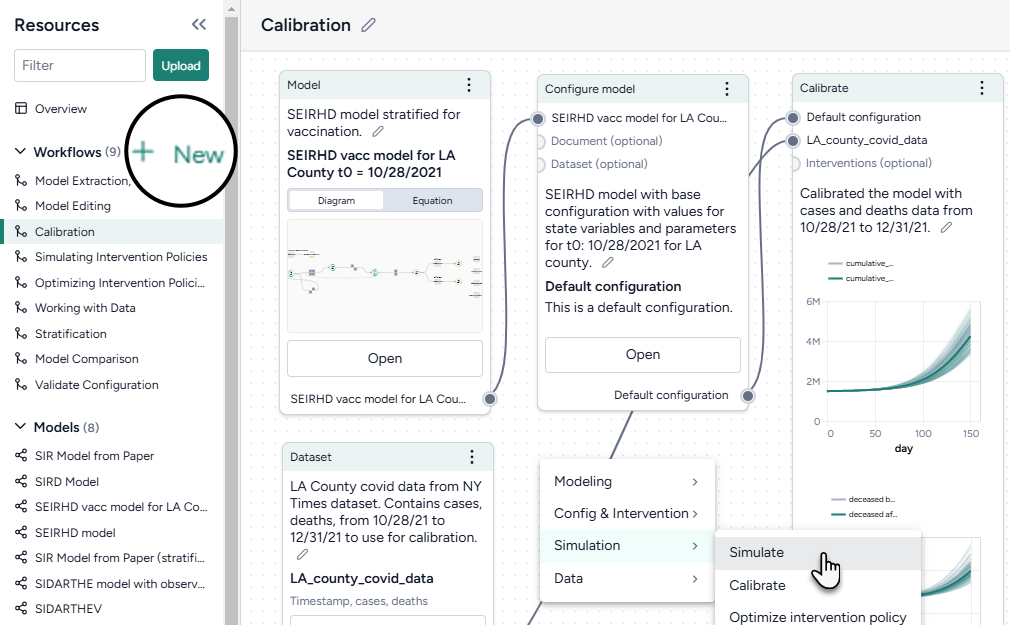
Each box is a resource or an operator that handles a task like transformation and simulation. They have a title, thumbnail preview, and optional annotations for capturing relevant context. Users can chain the outputs and inputs of resources and operators to:
- Recreate, reuse, and modify existing models and datasets to suit their modeling needs.
- Rapidly create scenarios and interventions by configuring, validating, calibrating, and optimizing models.
Templates
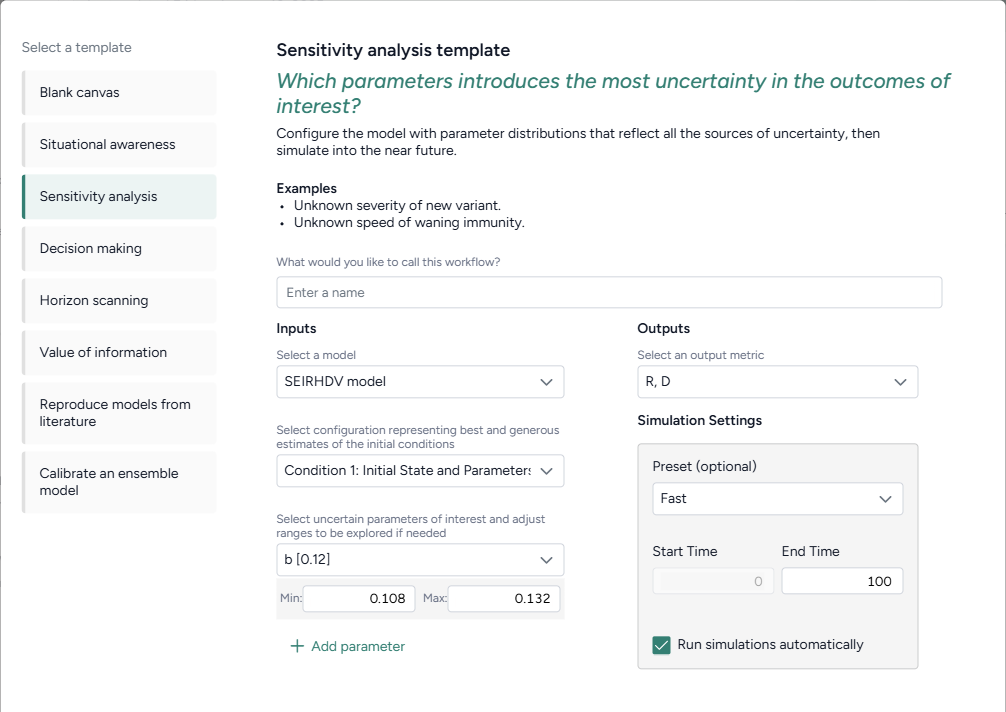
Workflow templates streamline the process of building common modeling workflows. They provide pre-configured and linked resources and operators tailored to user objectives, such as analyzing uncertainty, forecasting potential outcomes, or comparing intervention strategies. Available templates include:
- Situational awareness: Calibrate a model to historical data to obtain the best estimate of parameters for the present and then forecast into the near future.
- Sensitivity analysis: Configure a model with parameter distributions that reflect all the sources of uncertainty and then simulate into the near future.
- Decision making: Simulate a baseline scenario (with no interventions) and various scenarios with intervention policies and then show the relative impact of each policy compared to the baseline.
- Horizon scanning: Configure a model to represent the extremes of uncertainty for some parameters and then simulate into the near future with different intervention policies and compare the outcomes.
- Value of information: Configure a model with parameter distributions that reflect all the sources of uncertainty and then simulate into the near future with different intervention policies.
- Reproduce models from literature: Create models from extracted equations, configure them using extracted values, simulate to reproduce results, and—if multiple models are created—compare them.
- Calibrate an ensemble model: Simulate and calibrate several models individually and then calibrate the ensemble.
Configuring complex scientific tasks
Resources and operators in the workflow graph summarize the data and inputs/outputs that they represent. Users can drill down to view more details or settings.
Terarium’s operators support various ways for users to configure complex scientific tasks, including:
- A guided wizard for quickly configuring common settings.
- A notebook for direct coding.
- An integrated AI assistant for creating and refining code even if the user doesn’t have any programming experience.
Available operators include:
- Modeling
- Create model from equations: Build a model using LaTeX expressions or equations extracted from a paper.
- Edit model: Modify model states and transitions using an AI assistant.
- Stratify model: Divide populations into subsets along characteristics such as age or location.
- Compare models: Generate side-by-side summaries of two or more models or prompt an AI assistant to visually compare them.
- Config and intervention
- Configure model: Edit variables and parameters or extract them from a reference resource.
- Validate configuration: Determine if a configuration generates valid outputs given a set of constraints.
- Create intervention policy: Define intervention policies to specify changes in state variables or parameters at specific points in time.
- Simulation
- Simulate: Run a simulation of a model under specific conditions.
- Calibrate: Determine or update the value of model parameters given a reference dataset of observations.
- Optimize intervention policy: Determine the optimal values for variables that minimize or maximize an intervention given some constraints.
- Simulate ensemble: Run a simulation of multiple models or model configurations under specific conditions.
- Calibrate ensemble: Extend the calibration process by working across multiple models simultaneously.
- Data
- Transform dataset: Modify a dataset by explaining your changes to an AI assistant.
- Compare datasets: Compare the impacts of two or more interventions or rank interventions.